Lotus DNA Library Prep Kit
One kit. Flexible workflow. Endless applications.
The Lotus DNA Library Prep Kit enables streamlined preparation of high-quality next generation sequencing (NGS) libraries from double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). The kit uses enzymatic fragmentation to generate libraries suitable for PCR-free, PCR-amplified, and targeted sequencing applications on Illumina platforms.
- Get the uniform sample coverage you need without relying on expensive equipment
- Regain valuable time with a fast, simple workflow
- Create application-specific NGS libraries by adding IDT adapters and xGen products for target capture
The Lotus kit can be customized for your applications when combined with one of the many IDT adapter options (see Ordering section). Additionally, use of xGen hybridization capture products provides a complete NGS solution that takes you from sample preparation to sequencing.
Ordering
Have questions about Lotus Library Prep?
Our experts will make your next library prep experience a breeze. Just ask.
Product details
Applications
The Lotus DNA Library Prep Kit produces high-quality next generation sequencing (NGS) libraries that are suitable for many applications including:
- Whole genome sequencing (WGS)
- PCR-free sequencing
- Detection of germline inherited single nucleotide variations (SNVs) and insertions/deletions (indels)
- Hybridization capture of target sequences (e.g., the exome or transcripts of interest)
- Low frequency somatic variation detection of SNVs and indels
- RNA-seq starting with full-length, double-stranded cDNA input
- Metagenomic sequencing
Method
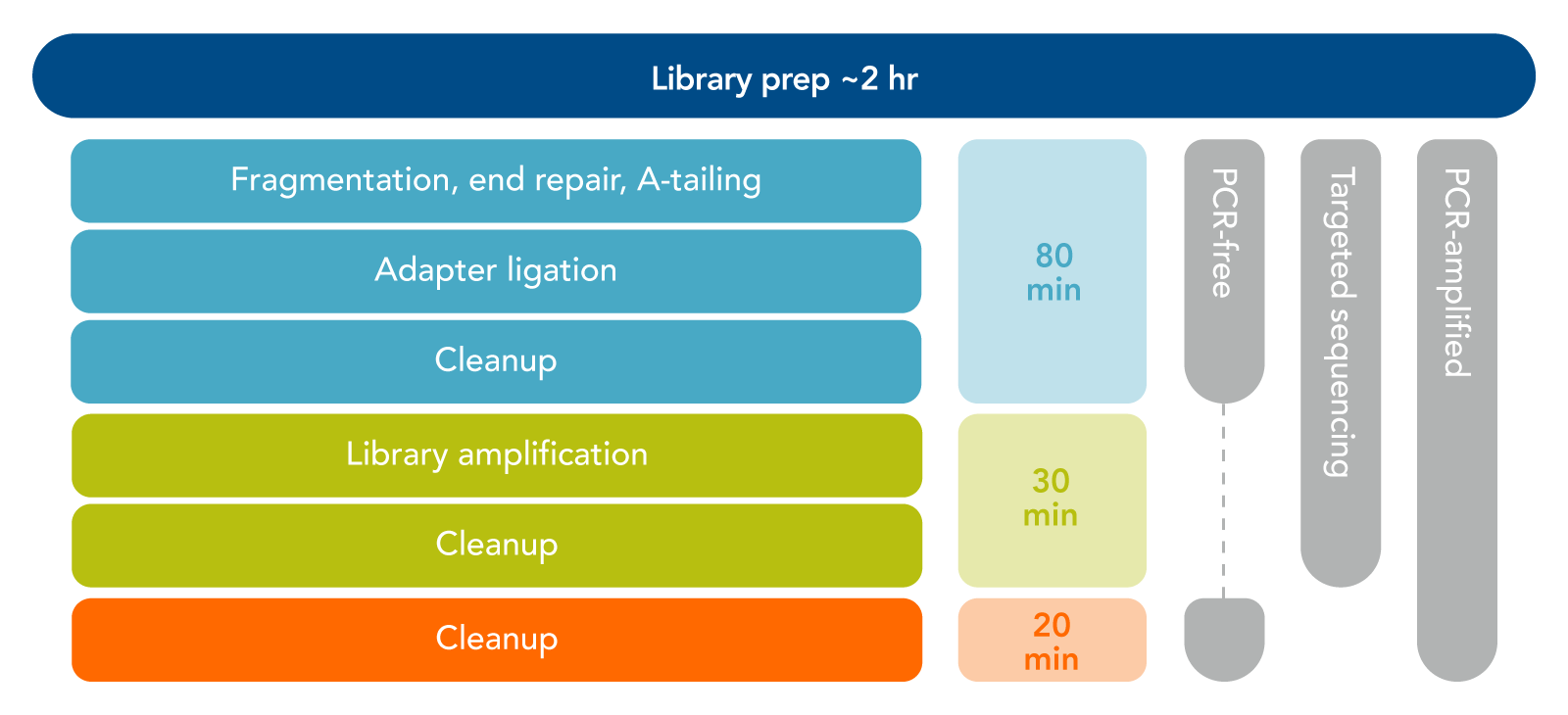
This kit involves minimal enzymatic incubations and bead-based purification steps, thereby reducing sample handling and overall library preparation time to under 2 hours. The major steps are depicted in Figure 1 and are summarized as follows:
- Enzymatic preparation. Fragmentation, end-repair, and dA-tailing of dsDNA are all performed in a single reaction.
- Ligation of either full-length or stubby P5 and P7 adapters. When using full-length adapters, the final PCR step is optional and can be used to increase library yield. However, stubby adapters (sometimes called truncated adapters) require amplification with primers to incorporate sample indexing sequences and to add the P5 and P7 sequences.
- Optional PCR amplification. Choose to amplify your libraries based on adapter and DNA input used. A bead-based cleanup removes oligonucleotides and small fragments after PCR.
Figure 1. Overview of Lotus DNA library preparation. Our easy enzymatic method takes you from sample to sequencing while eliminating the need for acoustic shearing methods that require instrumentation and extra time.
Kit overview
The Lotus kit comes with all the buffers, reagents, and enzymes needed for fragmentation, adapter ligation, and an optional PCR (to add index sequences, depending on adapter type, or to increase the amount of DNA for sequencing). You supply the DNA and add adapters that fit your goals. Table 1 provides additional specifications for using this kit.
Table 1. Specifications of the Lotus DNA Library Prep Kit.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Kit sizes | 16 reactions 96 reactions |
Sample types | Double-stranded DNA from fresh, frozen tissue Genomic DNA Full-length, double-stranded cDNA |
| DNA input range | 1–250 ng |
| Suggested DNA insert size | Whole-genome applications: 350 bp Hybridization capture: 200 bp |
| TA-ligation adapters (see Table 2) | Full-length: PCR amplification is optional Stubby (truncated): PCR is required to add index sequences |
Adapters
Complete your library prep with our selection of ready-to-use xGen UDI-UMI Adapters or xGen Stubby Adapter and UDI Primer Pairs (Table 2). We also offer many high-quality, custom adapters and index primers that are application-specific and ideal for use with the Lotus kit.
Table 2. How to choose IDT adapters for common applications when using the Lotus DNA Library Prep Kit.
| Application | Best choice | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Whole genome sequencing (WGS), metagenomics, PCR-free sequencing (≥100 ng input) | xGen UDI-UMI Adapters | Full-length adapters – required for PCR-free applications |
| WGS, metagenomics with PCR (1–250 ng input), exome sequencing, and targeted germline sequencing (SNVs, indels) | xGen Stubby Adapter and UDI Primer Pairs | Simple workflow – prepare your ligation master mix with a universal adapter and introduce unique dual index sample barcodes via PCR |
| Low-level mutation detection, down to ~1% frequency | xGen UDI-UMI Adapters | More sensitive – use UMI consensus analysis to remove sequencing errors |
| RNA-seq starting with full-length,
| xGen UDI-UMI Adapters | More quantitative – UMI is used to remove PCR duplicates |
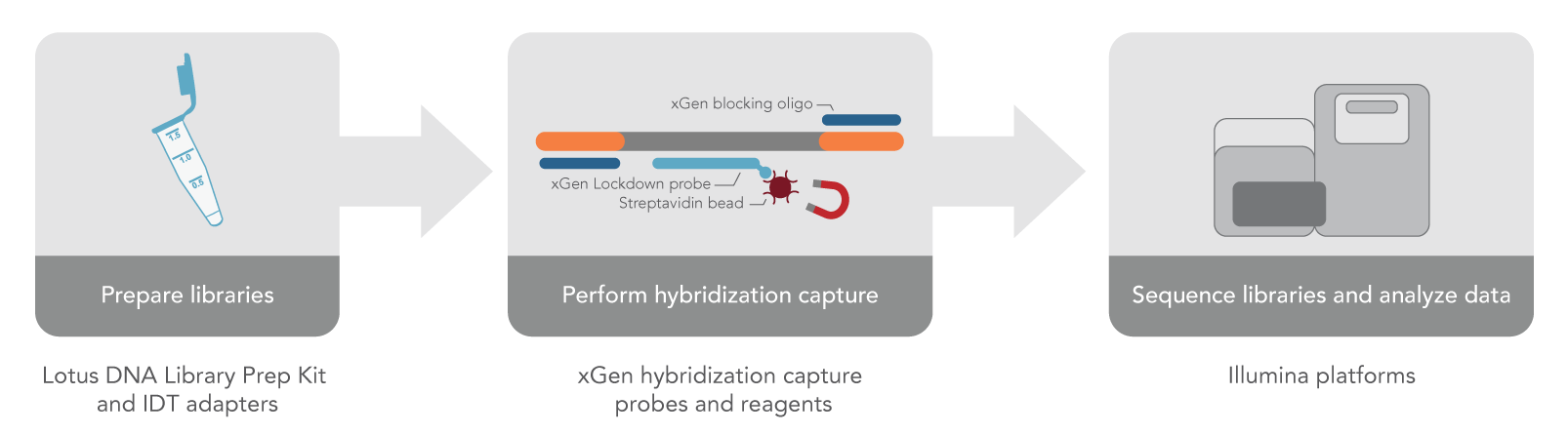
Complete workflow for hybridization capture experiments
Lotus DNA Library Prep Kit paired with adapters from IDT create libraries that are compatible with xGen hybridization capture probes and reagents for when you only need to perform targeted sequencing (Figure 2). Here is a list of the key components you will need:
- xGen Hybridization and Wash Kit
- xGen Universal Blockers—TS Mix or 10 bp TS Mix
- xGen Lockdown Panels and Probe Pools
- xGen Gene Capture Pools
- xGen Library Amplification Primers
Performance
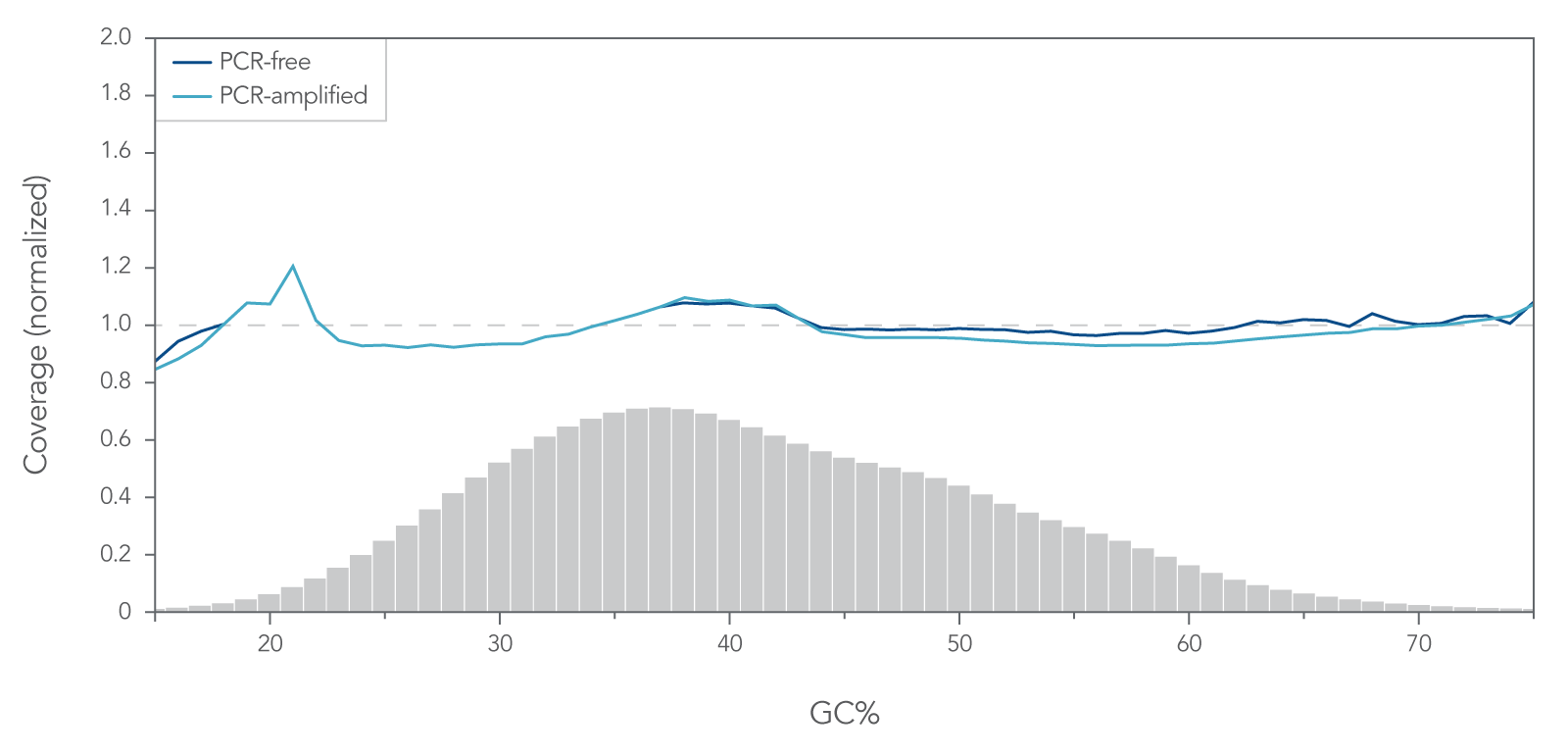
Uniform GC coverage from PCR-free and amplified libraries
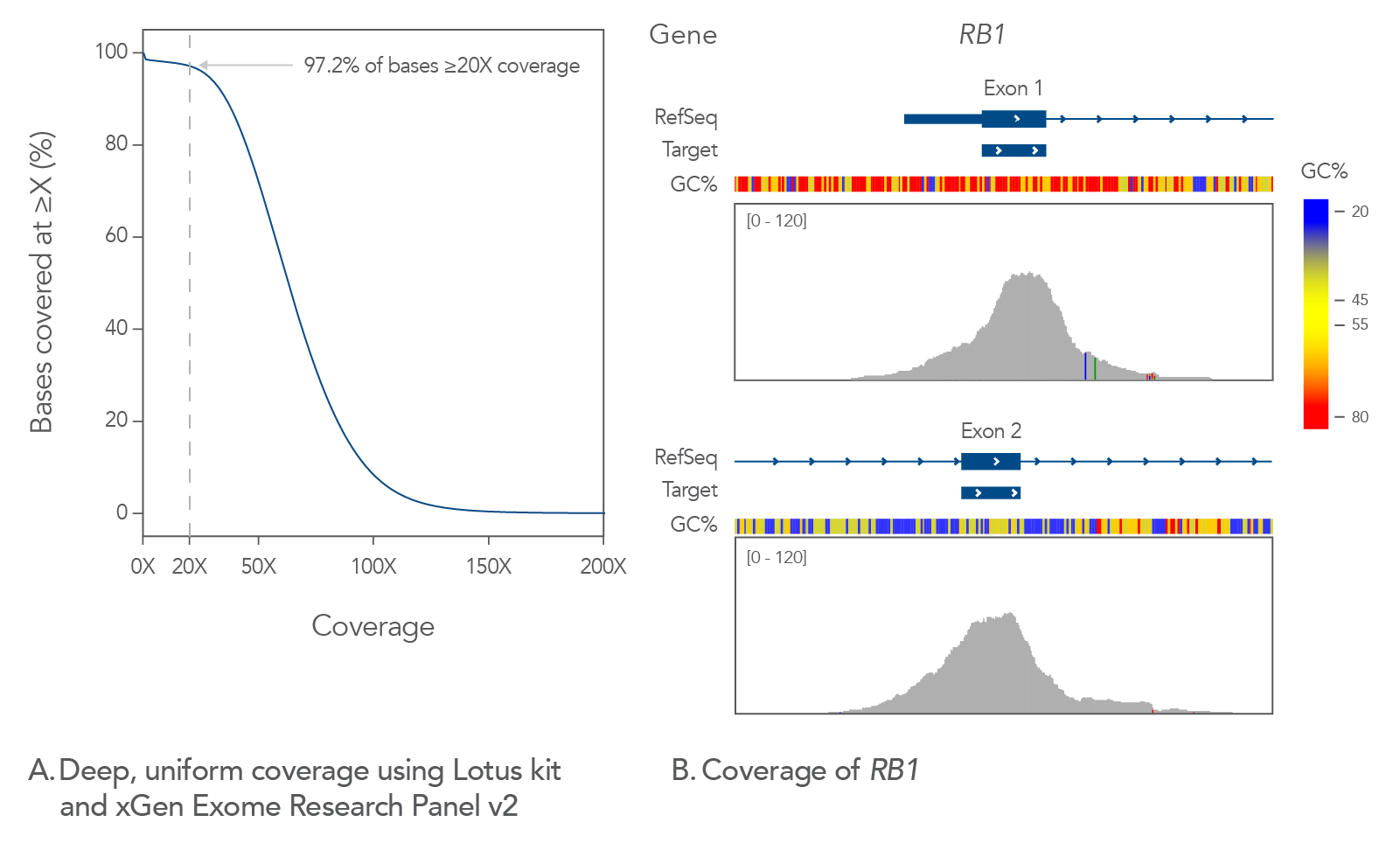
The Lotus DNA Library Prep Kit produces consistent genome coverage with low bias across samples (Figure 3).
Lotus DNA Library Prep offers superior coverage and uniformity for targeted sequencing
IDT adapters and xGen Lockdown Probes and Panels are manufactured using stringent, proprietary methods that are critical for producing high-quality oligos for NGS applications. When these adapters and hybridization capture probes are used with the Lotus Kit for targeted sequencing, results show consistent, highly uniform, sequence coverage (Figures 4–5).
xGen Stubby Adapter and Unique Dual Index Primer Pairs and were enriched in a single 12-plex capture using the xGen Exome Research Panel v2. The enriched libraries were sequenced (2x100) on a NextSeq® instrument (Illumina) and subsampled to 5 Gb. The data shows the mean coverage for the 12 libraries and indicates deep, uniform coverage with a flanked, on-target rate of 94.7%, mean target coverage of 64.5X and a duplication rate of 3.3% (calculated with Picard). (B) Exons 1 and 2 of RB1 show uniform, complete coverage on the Integrative Genomics Viewer. RB1 exons 1 and 2 show extremes of GC content with ~76% in exon 1 and ~38% in exon 2.
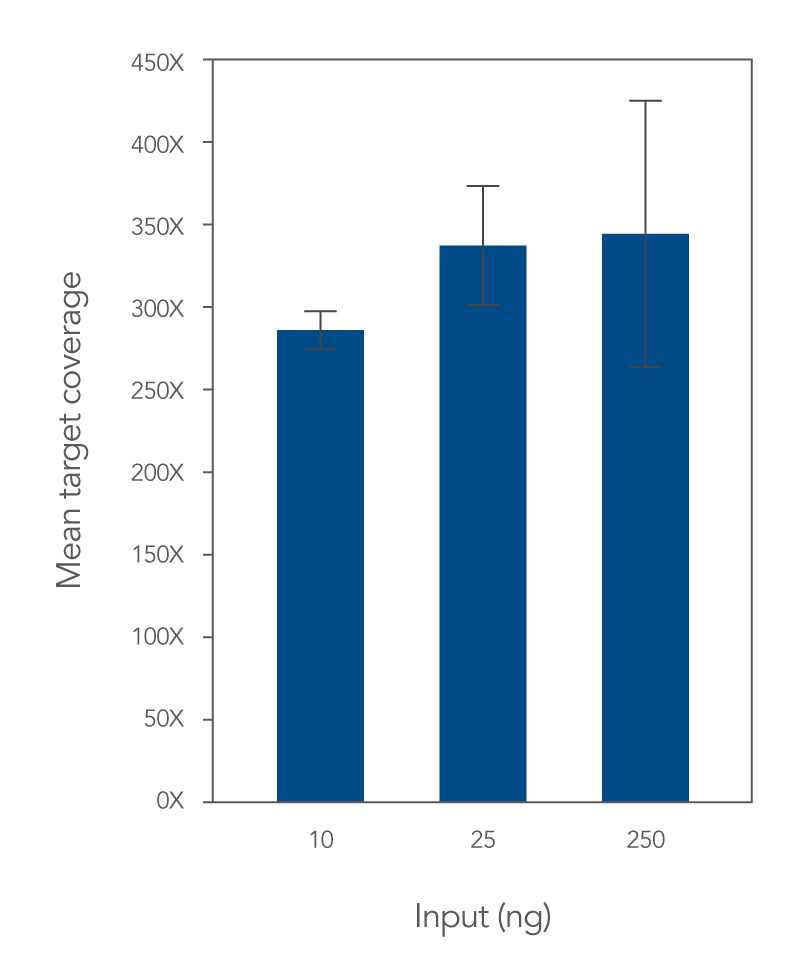
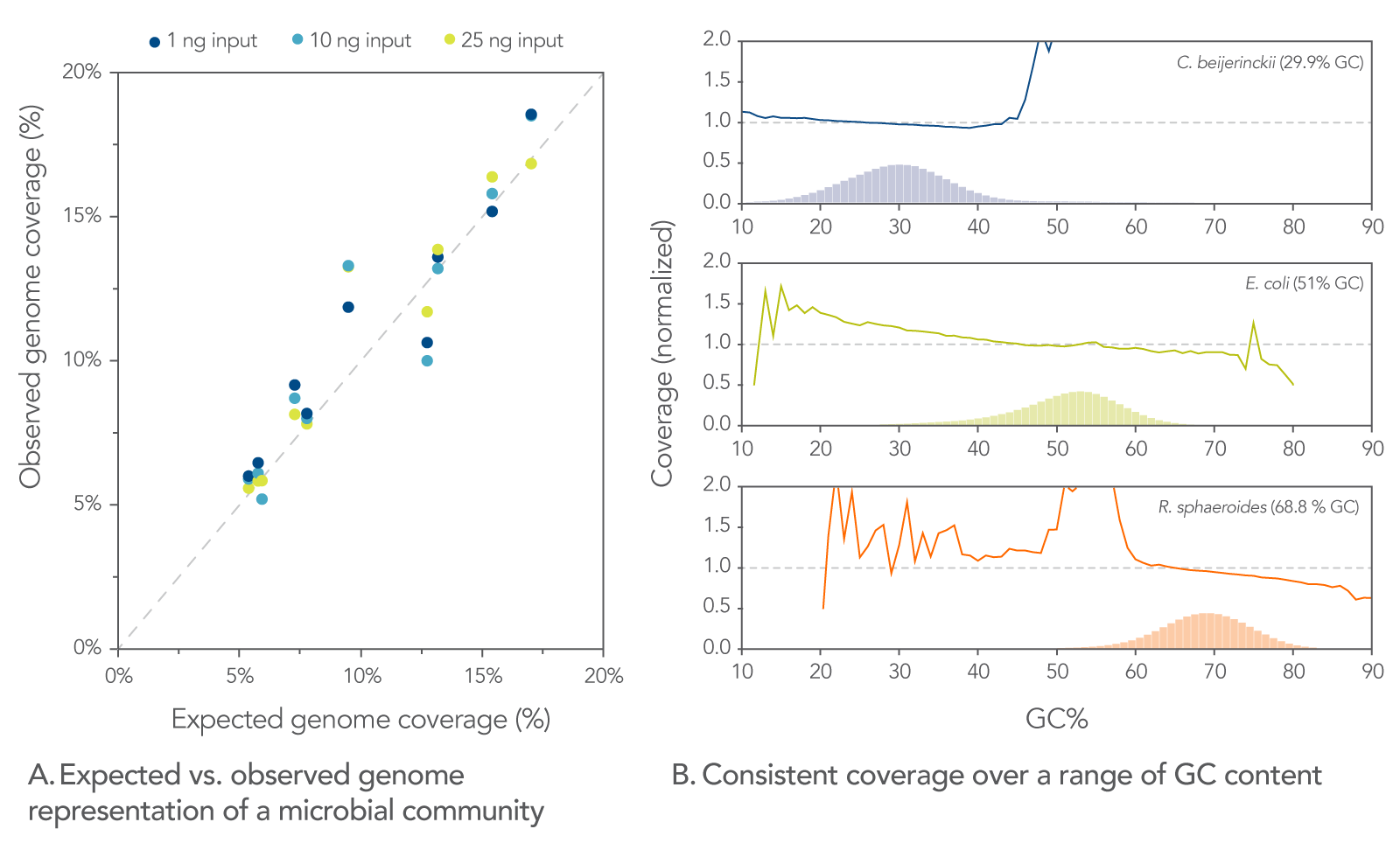
Superior representation of an artificial microbial community of 10 strains
The observed representation of each genome was consistent across a range of inputs (1, 10, and 25 ng) and correlated well with expected results (Figure 6A). Consistent genome coverage was observed across samples with varying levels of GC content (Figure 6B). The variability in size of the genomes, input amount, and GC content do not influence results.


 Processing
Processing